HeroSecondaryQuote
JSS component is missing React implementation. See the developer console for more information.
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, the ability to visualize, analyze, and optimize internal processes is more crucial than ever. Enter process mining—a cutting-edge data-driven technique that offers unparalleled insights into how businesses operate. By leveraging data from applications like CRM and ERP systems, process mining builds comprehensive models of end-to-end processes, enabling organizations to detect inefficiencies, compliance issues, and performance bottlenecks.
In this article, we’ll explore what process mining is, how it works, and what it can and can’t do for businesses looking to optimize their processes.
Jump to:
What is process mining?
Why is process mining important?
Types of process mining
How does process mining work?
Benefits of process mining
Limitations of process mining
Process mining examples
How is process mining different from task mining?
How does process mining work within process intelligence?
What is process mining?
Process mining is a data-driven technique used to understand, track, and improve processes by analyzing data from information systems.
Applications such as CRM and ERP systems as well as other systems of record automatically create event logs that record every action taken. The data in these logs can be collected or “mined” to create an audit trail of the processes the applications are involved in. This works even when multiple applications are used in a single process.
Process mining technology follows these audit trails to build a process model showing the details of the end-to- end process, as well as any variations. Business users can analyze these models to find out if the processes are functioning as they should and, if not, investigate the root causes of deviations from the optimal path.
Why is process mining important?
Process mining allows businesses to:
- Visualize and understand their processes in detail.
- Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, highlighting opportunities for improvement.
- Analyze process performance metrics in real-time to support resource allocation efforts.
- Improve compliance with internal and regulatory policies.
Businesses live by their processes, which are a prescribed set of actions employees take to get things done. When processes run well, the business runs well. When processes run poorly, the business faces various risks, from loss of revenue and customer dissatisfaction to compliance violations.
Most businesses have a general idea of how their processes should run but lack insight into the day-to-day details of execution. Without this data, a business cannot make impactful changes.
Types of process mining
Process discovery: Process discovery is a strategic technique for gaining a deep understanding of your organization's workflows. Think of it as a critical first step in visualizing and analyzing how your business processes function in their “as-is” state using process mining and task mining. Process discovery is a foundational element of process intelligence, which builds on the intelligence gained from process discovery through process analysis, process monitoring, process prediction, and process simulation.
Conformance checking: Conformance checking, another crucial pillar of process mining, ensures that business operations align with predefined models or standards. It acts as a quality assurance measure, highlighting discrepancies between expected and actual process behaviors. This technique is vital for organizations that aim for compliance and consistency. By comparing real execution data against process models, conformance checking identifies deviations and non-compliance issues.
Enhancement: Enhancement in process mining focuses on improving existing processes by leveraging insights gained from data analysis. This approach goes beyond identification and correction, aiming to elevate process performance to new heights. Enhancement integrates advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to optimize processes. By analyzing historical data, these technologies identify trends and predict outcomes, enabling organizations to make proactive improvements.
How does process mining work?
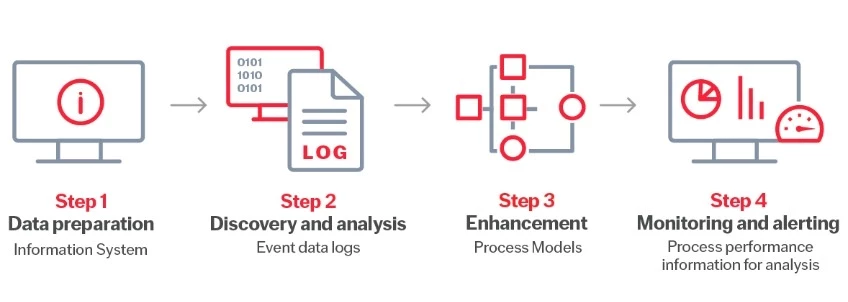
Before process mining, businesses had to do manual data reviews and interview stakeholders to find out how their processes were performing. This was often a slow, tedious process with a high margin of error. Process mining uses automation to depict real-world process performance accurately, faster, and more precisely than manual methods. There are four key steps to process mining:
Step 1: Data preparation
The first stage involves collecting event logs from various information systems such as ERP and CRM systems or workflow management tools. The data is cleaned to make sure it's consistent, complete, and doesn't contain duplicates.
Step 2: Discovery and analysis
During discovery, algorithms will automatically generate visual process models based on the real sequence of actions seen in the event logs. This will include timestamps for each step and any variations found in process flows.
Process analysis involves comparing the discovered process models with your optimal process models or business rules, to check whether the observed interactions match expected behavior. This step will highlight any missing activities, bottlenecks, or delays.
Step 3: Enhancement
Enhancement involves refining and optimizing the discovered process models using the insights you’ve gained and other data sources. This may involve reallocating resources, redesigning processes, or automating tasks to improve efficiency.
Step 4: Monitoring and alerting
The final stage is to establish monitoring mechanisms to track process performance and the impact of optimization efforts. By iterating through the process mining cycle and monitoring changes, businesses will see continuous improvements in operational efficiency, quality, and compliance.
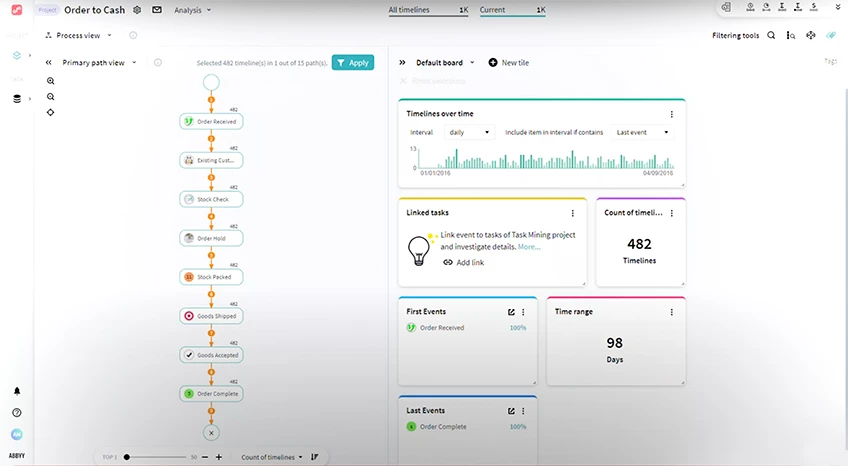
What are the benefits of process mining?
Process mining offers significant benefits to enterprises across all industries, including:
- Increased transparency: Process mining gives you accurate and objective insights on how your operational processes are running. This helps you to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and deviations.
- More data-driven decision-making: With access to detailed insights and performance metrics, businesses can confidently make decisions to optimize performance, backed by data.
- Increased efficiency: By identifying opportunities to simplify and automate processes, businesses can streamline workflows and reduce process lead times.
- Reduced costs: Improving business efficiency and resource allocation is one way process mining reduces costs. Process mining also works with your existing systems, so you don't need to invest in new applications to expand your operational capabilities.
- Enhanced customer experience: Identifying opportunities to simplify customer journeys and speed up internal processes will help you to improve your customers’ experience.
- Continuous improvement: Process mining isn't an isolated activity. It encourages continuous process improvement by enabling you to simulate proposed changes and providing feedback.

Limitations of process mining
Process mining offers enormous advantages over manual approaches to process analysis, but it has its limitations. For example:
- Evaluate complex processes: Process mining works well in simple scenarios yet lacks the sophistication to identify the root cause of complex processes with a large number of valid variations.
- Pin-pointing root cause: Traditional process mining identifies process-related issues but stops short of providing granular answers concerning the root causes of those issues.
- Evaluating complex processes: Basic process mining methods work well in simpler process scenarios, yet often lack the sophistication to evaluate ad-hoc and complex processes with a large number of variations.
- Analyzing in real-time: Process mining typically analyzes past performance rather than current performance, lacking the ability to monitor processes on an ongoing basis and alert users to deviations.
- Connecting to many data sources: Some traditional process mining tools may be limited in the types of data they can connect to, which can limit the value they provide.
All of these limitations of basic process mining solutions can be overcome with a comprehensive, modern, next-¬generation solution: enter process intelligence. Process intelligence solutions help businesses uncover and analyze root causes of problematic bottlenecks, can visualize any process, including messy and ad-hoc ones, and enable businesses to predict AND simulate potential process improvement measures. The most effective process mining solutions include process intelligence capabilities.
Process mining examples
Process mining is a technique that can be leveraged in any industry to gather insights into process execution and inefficiencies. Here are five use cases that demonstrate its versatility:
- Process mining in Insurance: Process mining can greatly improve efficiency and customer satisfaction in the insurance industry. By mapping out every step of a claim, from its initial submission to the final decision, process mining can highlight areas for improvement to achieve faster approvals with fewer errors. Process mining also helps you fine-tune your underwriting process, making sure you're assessing risks accurately and setting fair premiums while staying in line with changing regulations.
- Process mining in Healthcare: Organizations in the healthcare sector can use process mining to improve patient care pathways. Scrutinizing treatment protocols, processing times and resource allocation will help providers to spot process inefficiencies, from admission to discharge. Addressing these issues will reduce wait times, enhancing the overall quality of patient care.
- Process mining for Financial Services and Banking: Process mining can help financial services organizations to streamline their interorganizational processes, from loan processing to account auditing. By analyzing process flows, handling times and error rates, financial institutions will identify ways to improve their operational efficiency. This results in reduced costs and a better customer experience.
- Process mining in Transportation and Logistics: Process mining is crucial for optimizing supply chain operations, from procurement to delivery. Transportation and logistics providers can use it to identify bottlenecks and improve inventory management. With task mining, a distinct form of process mining, supply chain organizations can delve into users' interactions with their management systems, pinpointing recurring tasks and opportunities for automation.
- Process mining for Education: Process mining offers more than just insights into process inefficiencies. It also enables users to check engagement and interaction with critical systems. Educators can analyze the effectiveness of course curriculum by tracking student behaviors, such as how long they spend viewing class materials.
How is process mining different from task mining
Process discovery is the foundational step in understanding how a process actually operates, comprising process mining and task mining. Process mining is used for reconstructing processes from events recorded in logs, while task mining fills process gaps by mining user desktop activities. For example, a healthcare provider may use process mining to reconstruct the patient admission process by analyzing the electronic health record (EHR) system's event logs.
Simultaneously, task mining can be used to observe and analyze the actions of administrative staff on their desktops to fill in any gaps in the process not captured by the event logs. This comprehensive approach is essential for identifying bottlenecks, redundancies, and deviations, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and patient satisfaction.
How ABBYY Timeline helps in process mining
ABBYY Timeline is our market-leading process mining platform, built to power data-driven process improvement. Timeline process intelligence goes beyond process mining to offer businesses a comprehensive approach to achieving process excellence through five key capabilities:
Timeline helps you visualize your end-to-end process to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and outliers. With insight into your existing processes, you can make informed optimization decisions. Timeline’s process simulation feature enables you to test potential process changes and assess their business impact before implementation. Our low-code process mining platform comes with over 25 pre-built tools, so you can start analyzing your processes within minutes.
Ready to transform your business processes?
Frequently asked questions
What are the 3 types of process mining?
The three main types of process mining are:
- Discovery
Process discovery involves automatically generating process models from event logs. It aims to reveal the actual process flows recorded in the logs, without prior knowledge of the process. - Conformance
Conformance checking verifies whether the proposed process model is consistent with its real-world execution. This process mining method compares a process description with an existing process model using event log data, to identify deviations. - Enhancement
The aim of process enhancement (also referred to as an extension process or performance mining), is to optimize the quality and completeness of existing process models. For example, this might involve using data from a conformance check, along with other domain expertise, to remove a bottleneck.
How is AI used in process mining?
AI plays a critical role in process mining by automating several aspects of process discovery and optimization. For example:
- Discovery
At the initial process discovery stage, AI algorithms infer process models from event logs, reducing the need for manual modeling. - Conformance
Anomaly detection, powered by AI, identifies process deviations or irregularities in the discovered models. This data shows enterprises’ opportunities to streamline processes. - Enhancement
AI technologies automate repetitive tasks found at the conformance checking stage. Predictive analytics models then leverage AI to forecast future process behavior and outcomes, based on proposed changes. This allows users to proactively decide next steps.
What’s the difference between process mining and RPA?
Both process mining and robotic process automation (RPA) aim to optimize business processes. However, they serve distinct purposes, and are used at different stages of the process improvement lifecycle.
Process mining is a technique used to analyze event data, with the goal of understanding and optimizing processes. It uses algorithms to holistically visualize end-to-end processes, providing insights on execution and performance. In contrast, RPA automates repetitive tasks by deploying software robots to perform predefined processes, boosting efficiency and reducing manual effort.
In summary, process mining focuses on understanding how processes unfold, while RPA automates rule-based, repeatable tasks.
Subscribe for blog updates
RelevantBlogPosts
JSS component is missing React implementation. See the developer console for more information.
ConnectWithUs
JSS component is missing React implementation. See the developer console for more information.

